Stochastics Indicator
Updated 01/31/14
Stochastics is a technical indicator developed by George Lane. Its primary application has been in the timing of quick moves in the futures markets.
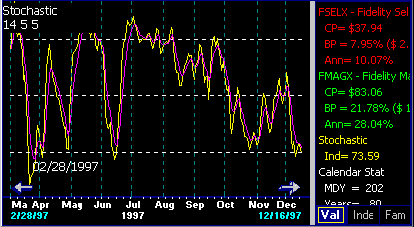
Stochastics works well when prices are trendless.
Disclaimer: No technical indicator can assure profits. As market conditions change, the interpretation and use of the indicator must change.
Stochastics is a technical indicator developed by George Lane. Its primary application has been in the timing of quick moves in the futures markets. This section describes FastTrack's Stochastics in "standard" terms so as to relate FastTrack to other technical analysis texts.
Mechanics of Stochastics
Stochastics in futures applications works on the principle that prices close near the top of the trading-range during uptrends and close near the bottom of the range during downtrends. Mutual funds, however, do not have a daily trading-range and they trade in much less volatile patterns. FastTrack offers a multi-day formulation of Slow Stochastics that is appropriate for fund characteristics.